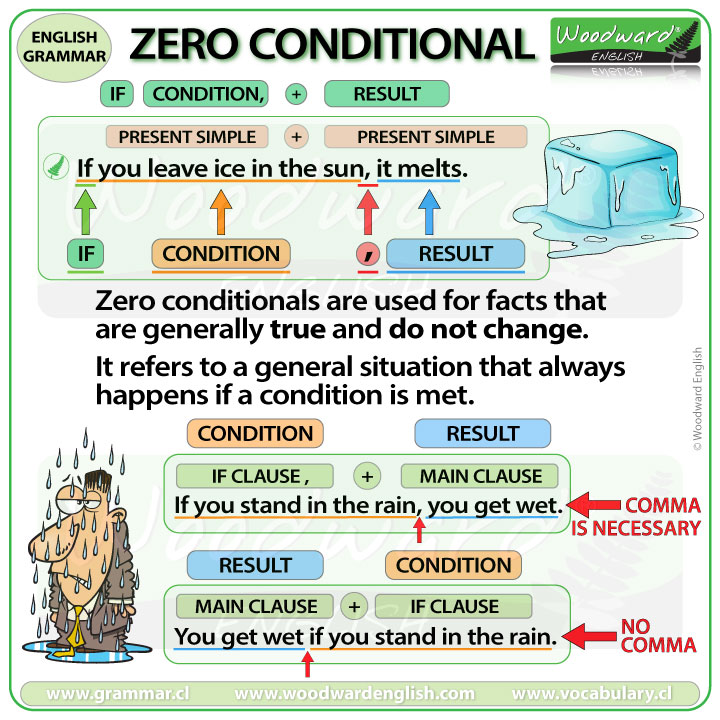
⤗ZERO CONDITIONAL
↬In English there are several types of conditions, including conditional zero. This type of conditional is used in situations where if a condition is met, the same result always occurs.
↬The zero conditional has the following structure:
⇏If + subject + present simple, subject + present simple
↬The order of the two sentences that make up the conditional structure can be changed. If we start with the condition (If), we will separate them with a comma. If we start with the phrase that expresses the result, it is not necessary to put the comma.
➼If water reaches 100ºC, it boils.
➼Water boils if it reaches 100ºC.
⇴In addition to true facts, zero conditional can also be used to give instructions. In this case we will use an imperative to express the instruction or warning.
EXAMPLES
- If you heat ice, it melts.
- Ice melts if you heat it.
- When you heat ice, it melts.
- Ice melts when you heat it.
- If it rains, the grass gets wet.
- The grass gets wet if it rains.
- When it rains, the grass gets wet.
- The grass gets wet when it rains.
⤠FIRST CONDITIONAL
➤This type of conditional is used in situations where if a condition is met, a given result is likely to occur.
➽If you don't put on repellent, you'll get bitten.
➡If you study hard, you'll get good marks.
↬The first conditional has the following structure:
⇴If + subject + present simple, subject + future simple
⍆We mostly use the simple future with will, but you can also use the simple future with going to or a modal verb: can, might, should, or must.
| FIRST CONDITIONAL | |
|---|---|
| WILL | If the weather is nice on Sunday, we'll go on a picnic.Si el domingo hace buen tiempo, iremos de picnic. |
| GOING TO | If I don't have to go to work tomorrow, I am going to visit my parents.Si mañana no tengo que ir a trabajar, iré a visitar a mis padres. |
| CAN | If the meeting finishes early, we can go for a drink.Sí la reunión termina temprano, podemos ir a tomar algo. |
| MIGHT | If I have time this afternoon, I might wash my car.Si esta tarde tengo tiempo, puede que lave el coche. |
| SHOULD | If they invite you, you should go.Si te invitan, deberías ir. |
| MUST | If you have any problems, you must call me.Si tienes algún problema, debes llamarme. |
⟷The order of the two sentences that make up the conditional structure can be changed. If we start with the condition (If) we will separate them with a comma. If we start with the phrase that expresses the result it is not necessary to put the comma.
⟿If the plane is delayed, she will be late.
⤀She will be late if the plane is delayed.
EXAMPLES
- If it rains, I won't go to the park.
- If I study today, I'll go to the party tonight.
- If I have enough money, I'll buy some new shoes.
- She'll be late if the train is delayed.
- She'll miss the bus if she doesn't leave soon.
- If I see her, I'll tell her.
⤐SECOND CONDITIONAL
➜This type of conditional is used to talk about events that are unlikely to happen in the future.
➞The structure of the second conditional
➨The second conditional has the following structure:
⟴If + subject + past simple, subject + would + verb in infinitive (without to)
Although with the personal pronouns I, he, she, and it the form was used as past tense of the verb TO BE, in the conditional form, the form were used. You could also use could instead of would.
| SECOND CONDITIONAL | |
|---|---|
| I | If I were invisible for one day, I could play tricks on my friends.Si yo fuera invisible por un día, les podría gastar bromas a mis amigos. |
| HE | If he weren't so stubborn, he would admit he was wrong.Si no fuera testarudo, admitiría que estaba equivocado. |
| SHE | If she were a good friend, she would help you.Si fuera una buena amiga, te ayudaría. |
| IT | If it were cheaper, I could buy it.Si fuera más barato, lo podría comprar. |
⏪The second conditional is used for situations in which the speaker considers it unlikely to happen in the future.
⏪For situations that are not true at the present time.
⏪To give advice to someone using the expression If I were you.

EXAMPLES
- If I won the lottery, I would buy a big house.(I probably won't win the lottery)
- If I met the Queen of England, I would say hello.
- She would travel all over the world if she were rich.
- She would pass the exam if she ever studied.(She never studies, so this won't happen)




No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario